SOURCE’s Project Assessment Tool allows governments to evaluate their projects against national and international methodologies. SOURCE enables the digitalisation of multiple project evaluation standards, allowing governments to easily assess their infrastructure projects in a single IT system, avoiding double data entries.
The Project Assessment is a unique functionality in SOURCE that allows users to derive a score or qualitative assessment against multiple criteria based on the data entered during the preparation of their projects.
National evaluation criteria
The integration process of SOURCE includes the digitalisation of the national project screening process. This streamlines the approval processes while facilitating more informed decision-making and effective planning. So far, SIF digitalised 10 national methodologies from 8 countries. In addition, SOURCE embeds international methodologies from the private sector and development finance institutions, empowering governments to evaluate their projects against international standards in one environment seamlessly.
International standards
The common framework of SOURCE and its 40 sector-specific guidance templates enables a better alignment of projects with international best practices and accommodates the required data collection to evaluate the projects against multiple methodologies and assessment criteria. SOURCE includes the private sector project information requirements facilitating a common language and the possibility for governments to promote online a pipeline of well-developed projects including the assessment results.
SIF (Sustainable Infrastructure Foundation) digitalised or is digitalising 16 methodologies. These methodologies range from national approaches to international methods such as the QII (Quality Infrastructure Investment) Indicators from the G20 and the FAST-Infra Label from FAST-Infra Group.
List of International Project Assessment methodologies digitalised in SOURCE
| Assessment methodology | |
| International Methodologies | Owned by |
| FAST-Infra Label (beta version) | FAST-Infra Group |
| Gap Fund | Gap Fund (EIB-GIZ) |
| GRIS (green, resilient, inclusive, and sustainable) | Asian Development Bank (ADB) |
| PDT (Project Development Tool) Checklist
(in development in SOURCE) |
Sustainable Markets Initiative (SMI) |
| PIERS (PPP and Infrastructure Evaluation and Rating System)
(in development in SOURCE) |
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) |
| QII (Quality Infrastructure Investment) Indicators (in development in SOURCE) | G20 |
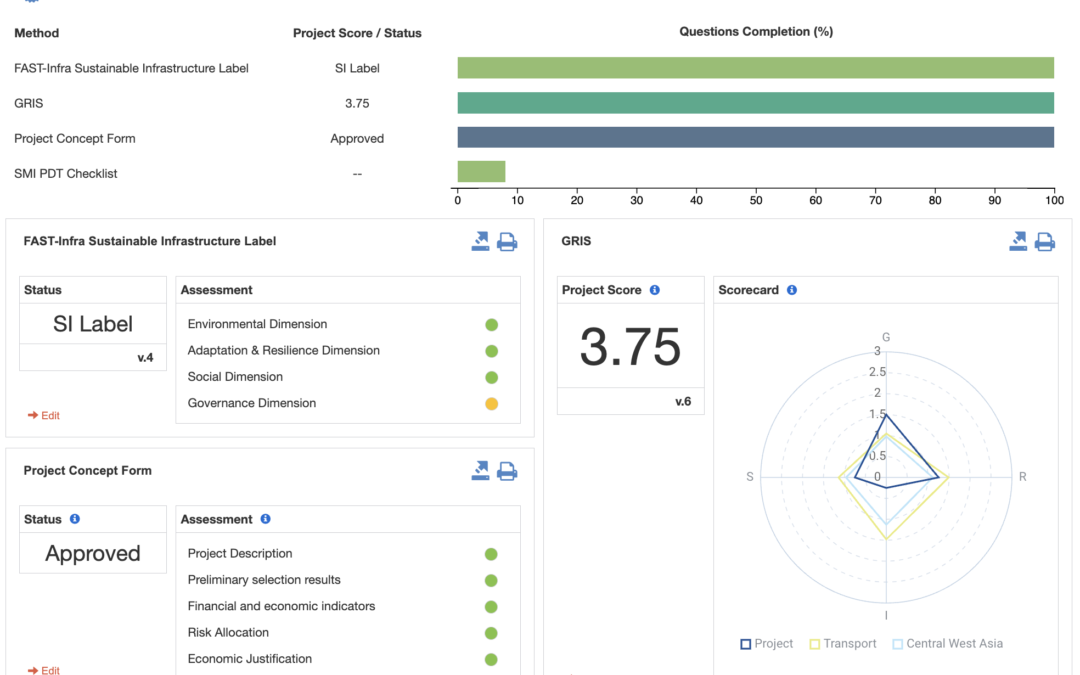
There are two distinct types of assessment available:
- Discrete: that computes an overall project score and individual scores per principles, represented in a spider chart (see Figure 1); and
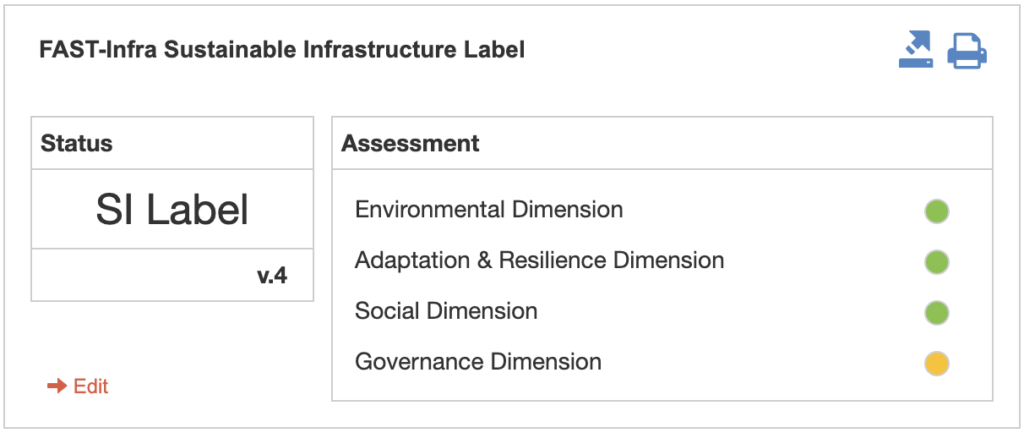
- Decision: that allows the assessment of criteria corresponding to a colour code (e.g. green/amber/red), leading to a final evaluation/decision (e.g. “approved”) (see Figure 2).
Figure 1 – Example of a methodology of type ‘Discrete”
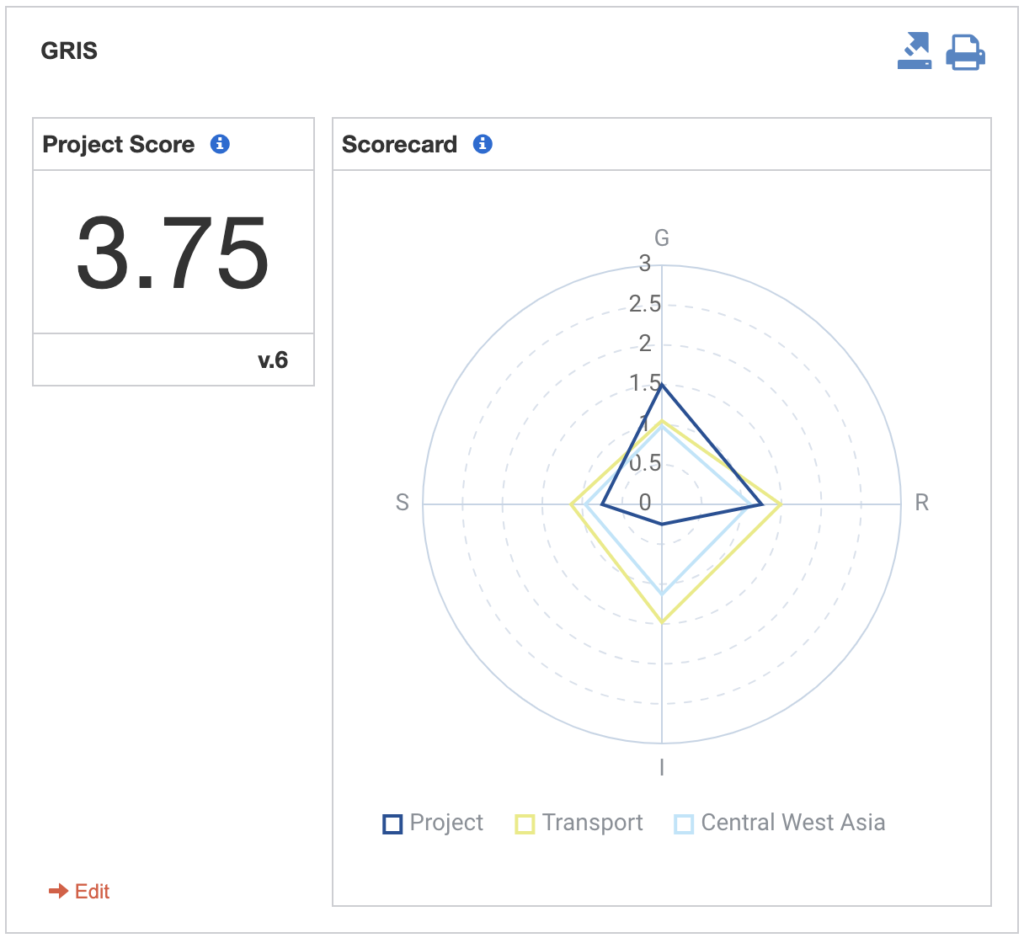
Figure 2 – Example of a methodology of type ‘Decision”
Main tab with the status and assessment criteria
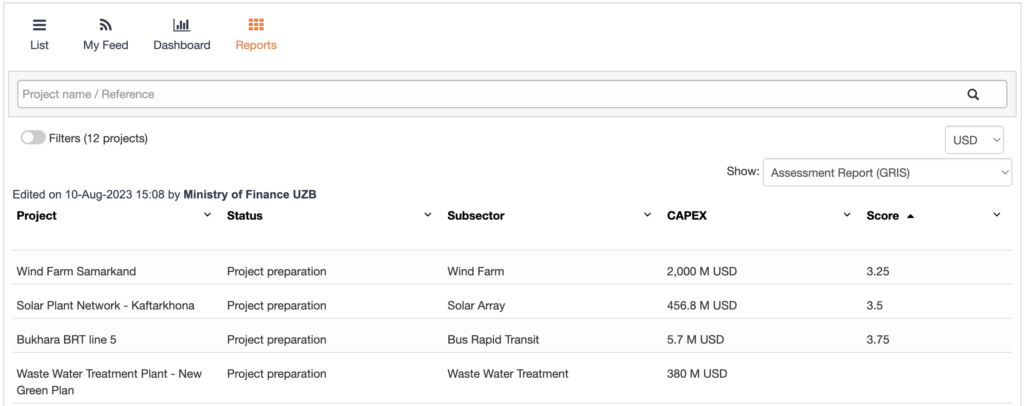
The project assessment methodology also allows governments to score their projects and later on analyse and decide their priorities based on the scores of the projects. SOURCE’s report tab allows governments to visualise all their projects according to different methodologies scores (See Figure 3).
Figure 3 – Example of how governments can monitor and prioritise projects based on the assessment results (example of SOURCE’s test environment)